Ag2ga40
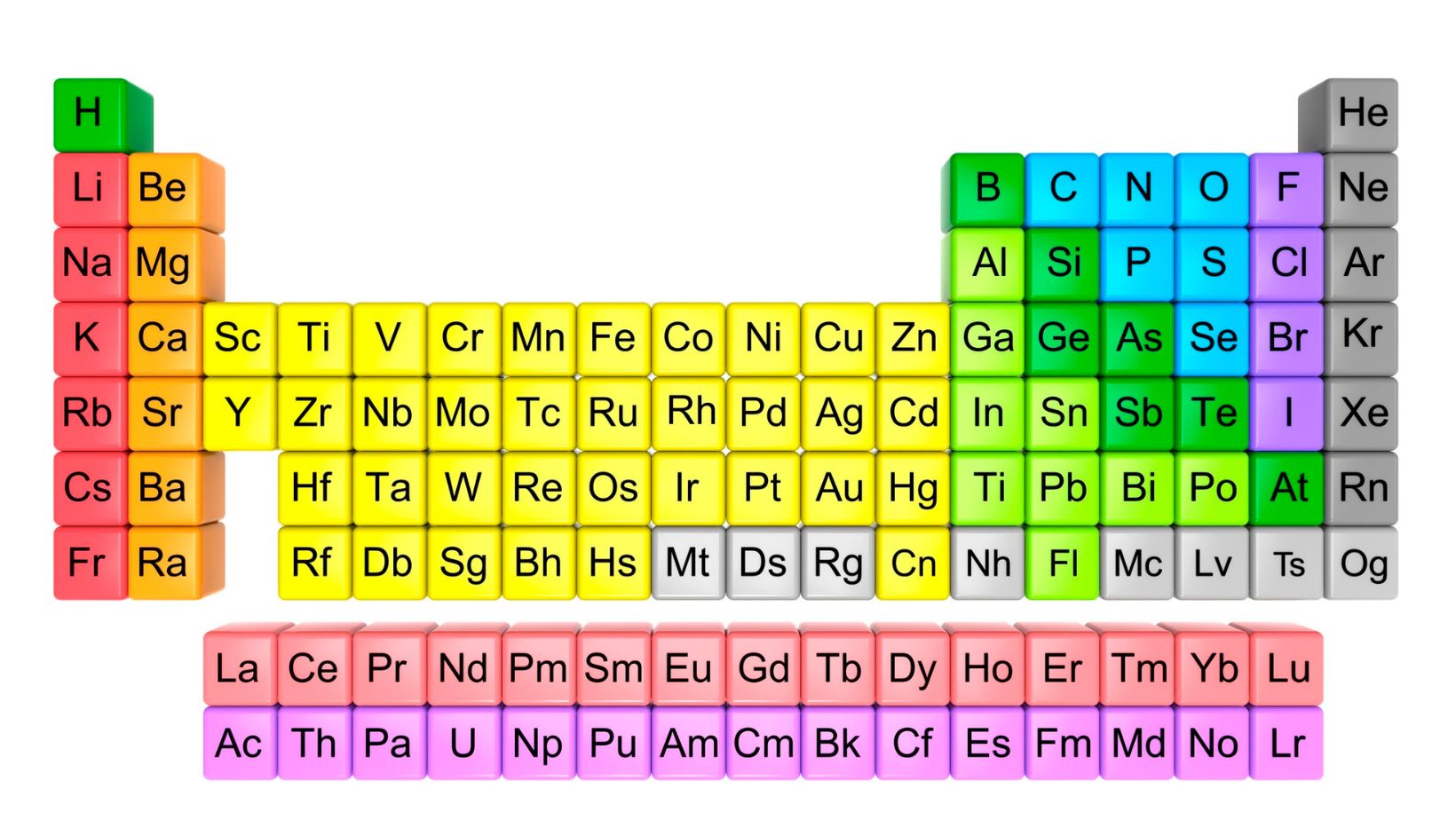
The Periodic Table is a foundational tool in the field of chemistry, providing a comprehensive overview of all known elements and their respective properties. It serves as a visual representation of the building blocks that make up our universe, offering valuable insights into the behavior and characteristics of different elements.
Within the Periodic Table, each element is organized based on its atomic number, which represents the number of protons found in its nucleus. This arrangement allows us to identify patterns and trends among elements, such as their reactivity, electron configuration, and chemical bonding tendencies.
The components of the Periodic Table Ag2ga40 include groups (or columns) and periods (or rows), each with distinct characteristics. Groups are arranged vertically and share similar properties due to their identical outer electron configurations. On the other hand, periods indicate an increase in atomic number from left to right across the table.
The History of the Periodic Table
Let’s delve into the fascinating history of the Periodic Table Ag2ga40 and explore how it has evolved over time, shaping our understanding of the elements and their components.
- The Early Beginnings: The journey of the Periodic Table dates back to the early 19th century when scientists began to recognize patterns in chemical elements. In 1803, John Dalton proposed his atomic theory, which laid the foundation for organizing elements based on their atomic weights. However, this initial attempt was far from perfect and lacked a comprehensive structure.
- Mendeleev’s Stroke of Genius: In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev revolutionized our understanding of elements by creating a more refined version of the Periodic Table. He arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight while also considering their chemical properties. This breakthrough led to the discovery of missing elements and predicted those yet to be found.
- Advancements in Modern Times: As scientific knowledge expanded, so did our understanding of atomic structures and properties. With further advancements in technology, such as X-ray crystallography and spectroscopy, scientists gained deeper insights into element classification. The development of quantum mechanics provided a solid theoretical foundation for explaining electron configurations within atoms.
- The Standard Periodic Table: Today, we use a standard version known as the “long form” or “18-column” periodic table developed by Glenn T. Seaborg in 1945-46. It organizes elements based on their atomic numbers (the number of protons), allowing for a more accurate representation that aligns with modern scientific discoveries.
- Unifying Elements Across Borders: The significance of the Periodic Table extends beyond scientific boundaries; it unifies researchers worldwide regardless of language or nationality. Its universal symbol system allows scientists from different countries to communicate effectively about various chemical phenomena.
- Future Prospects: The Periodic Table continues to evolve as new elements are synthesized and discovered. With ongoing research, scientists strive to uncover the properties and potential applications of these newly added elements, expanding our understanding of the building blocks of matter.
In conclusion, the history of the Periodic Table is a testament to human curiosity, scientific exploration, and the quest for knowledge. From its humble beginnings to its current form, this iconic tool has played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of elements and their components. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of chemistry, we can only anticipate further revelations that will enhance our comprehension of the intricate world of atoms and molecules.
Key Contributors to the Development of the Periodic Table
When it comes to the development of the Periodic Table, there have been several key contributors who played a significant role in shaping our understanding of chemical elements and their properties. Let’s take a closer look at some of these remarkable individuals:
- Dmitri Mendeleev: One cannot discuss the Periodic Table without mentioning Dmitri Mendeleev. In 1869, Mendeleev created the first version of the Periodic Table as we know it today. He arranged elements based on their atomic mass and observed patterns in their properties. His visionary approach allowed him to predict the existence and properties of undiscovered elements, leaving gaps for them in his table.
- Henry Moseley: In the early 20th century, Henry Moseley made significant contributions to our understanding of atomic structure and laid the foundation for modern periodicity. Through his experiments with X-rays and spectroscopy, Moseley discovered that each element has a unique number of protons in its nucleus, which we now refer to as its atomic number. This led to rearranging elements on the basis of atomic number rather than atomic mass.
- Glenn T. Seaborg: Another notable figure is Glenn T. Seaborg, who made groundbreaking discoveries related to transuranium elements (elements with atomic numbers greater than uranium). Seaborg’s work expanded our knowledge about these synthetic elements and earned him a Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1951.
- Marie Curie: While primarily known for her pioneering research on radioactivity, Marie Curie also contributed indirectly to our understanding of radioactive elements’ placement within the Periodic Table. Her discoveries paved the way for further advancements in nuclear chemistry.
- Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner: Although not as well-known as some other contributors, Döbereiner made an important contribution by identifying triads—groups of three elements with similar chemical properties. He noticed that the atomic weight of the middle element in each triad was roughly the average of the other two.




